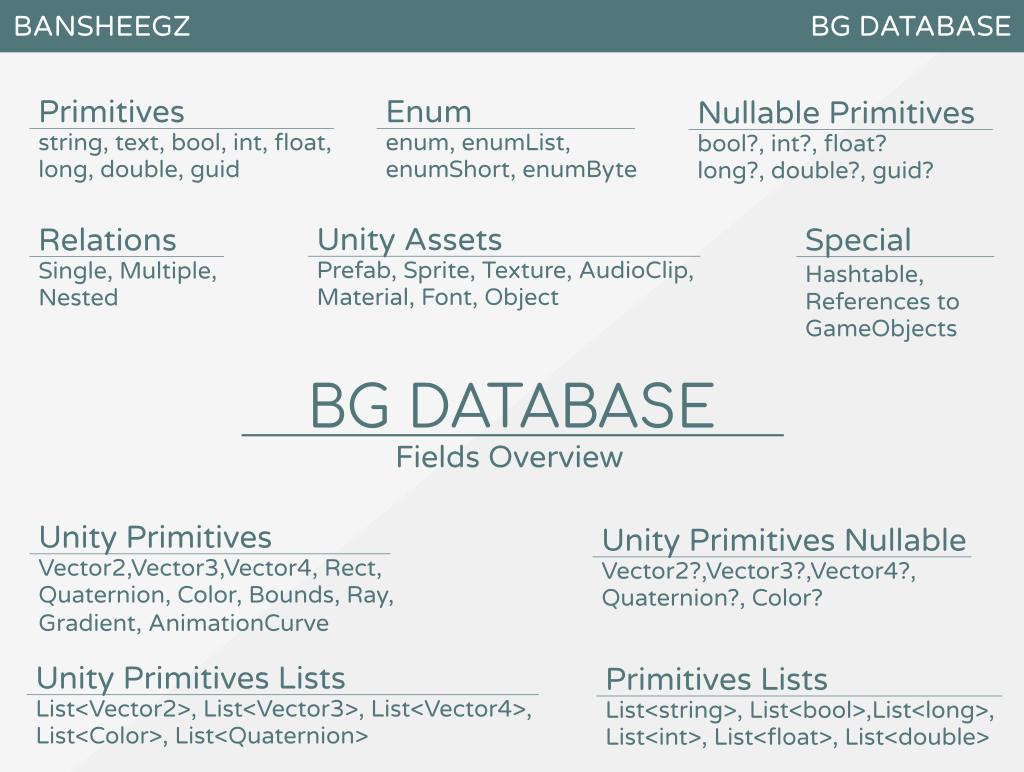
Fields overview
Fields table
This is all fields types, BGDatabase currently supports (you can create your own field if it's needed.)
| Field Group | Field name | Field Type | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primitives | int | int | |
| long | long | ||
| float | float | ||
| double | double | ||
| bool | bool | ||
| decimal | decimal | ||
| short | short | ||
| byte | byte | ||
| guid | Guid | ||
| dateTime | DateTime | ||
| string | string | single line text | |
| text | string | multiple lines text | |
| Primitive nullable | int? | int? | |
| long? | long? | ||
| float? | float? | ||
| double? | double? | ||
| bool? | bool? | ||
| guid? | Guid? | ||
| Enum #5 | enum | Enum | |
| enumByte | Enum | ||
| enumShort | Enum | ||
| enumList | List<Enum> | ||
| Unity Primitives | vector2 | Vector2 | |
| vector3 | Vector3 | ||
| vector4 | Vector4 | ||
| quaternion | Quaternion | ||
| rect | Rect | ||
| bounds | Bounds | ||
| color | Color | ||
| ray | Ray | ||
| ray2d | Ray2D | ||
| keyCode | KeyCode | ||
| gradient | Gradient | ||
| animationCurve2017 | AnimationCurve | Field target Unity 2017. For Unity >= 2018, download field animationCurve2018 here | |
| Unity Primitive nullable | vector2? | Vector2? | |
| vector3? | Vector3? | ||
| vector4? | Vector4? | ||
| quaternion? | Quaternion? | ||
| color? | Color? | ||
| Unity Assets #6 | unityTexture | Texture | |
| unityTexture2d | Texture2D | ||
| unitySprite | Sprite | Can accept a single sprite, a sprite from a multiple sprite, a sprite from SpriteAtlas If you use SpriteAtlas, make sure to turn SpritePacker on (set Edit->Project settings->Editor->SpritePacker to "Always Enabled" and press on "Pack preview" button when you change your atlas) | |
| unityMaterial | Material | ||
| unityPrefab | GameObject | ||
| unityFont | Font | ||
| unityAudioClip | AudioClip | ||
| unityObject | Object | Any Unity asset type can be referenced. Additional type constraint can also be added and Code Generators generate proper property type | |
| List of Primitives | listBool | List<bool> | |
| listDouble | List<double> | ||
| listFloat | List<float> | ||
| listGuid | List<Guid> | ||
| listInt | List<int> | ||
| listLong | List<long> | ||
| listString | List<string> | ||
| List of Unity Primitives | listVector2 | List<Vector2> | |
| listVector3 | List<Vector3> | ||
| listVector4 | List<Vector4> | ||
| listQuaternion | List<Quaternion> | ||
| listColor | List<Color> | ||
| Dictionary | hashtable #4 | Hashtable | |
| Relations #1 | relationSingle | BGEntity | reference to one single row from one single table |
| relationMultiple | List<BGEntity> | reference to several rows from one single table | |
| manyTableRelationSingle | BGEntity | reference to one single row from several tables (use field's gear icon to define multiple tables). Not recommended, use viewRelationSingle instead | |
| manyTableRelationMultiple | List<BGEntity> | reference to several rows from several tables (use field's gear icon to define multiple tables). Not recommended, use viewRelationMultiple instead | |
| viewRelationSingle | BGEntity | reference to one single row from a view (several tables) | |
| viewRelationMultiple | List<BGEntity> | reference to several rows from a view (several tables) | |
| nested #2 | List<BGEntity> | read-only | |
| Unity Scene #3 | objectReference | BGWithId | read-only |
| objectListReference | List<BGWithId> | read-only | |
| objectListMultiValueReference | List<BGWithId> | read-only | |
| Calculated #7 | calculatedBool | bool | These fields calculate the value, when this value is requested, using graph editor tool |
| calculatedString | string | ||
| calculatedInt | int | ||
| calculatedFloat | float | ||
| calculatedLong | long | ||
| calculatedDateTime | DateTime | ||
| calculatedObject | object | ||
| action | Action | Action does not calculate any value, but change database values, create/delete rows. | |
| Programmable #8 | programmableBool | bool | Alternative to calculated fields, but calculation is implemented with C# code, rather than the graph tool. |
| programmableString | string | ||
| programmableInt | int | ||
| programmableFloat | float | ||
| programmableObject | object |
Relational fields (#1)
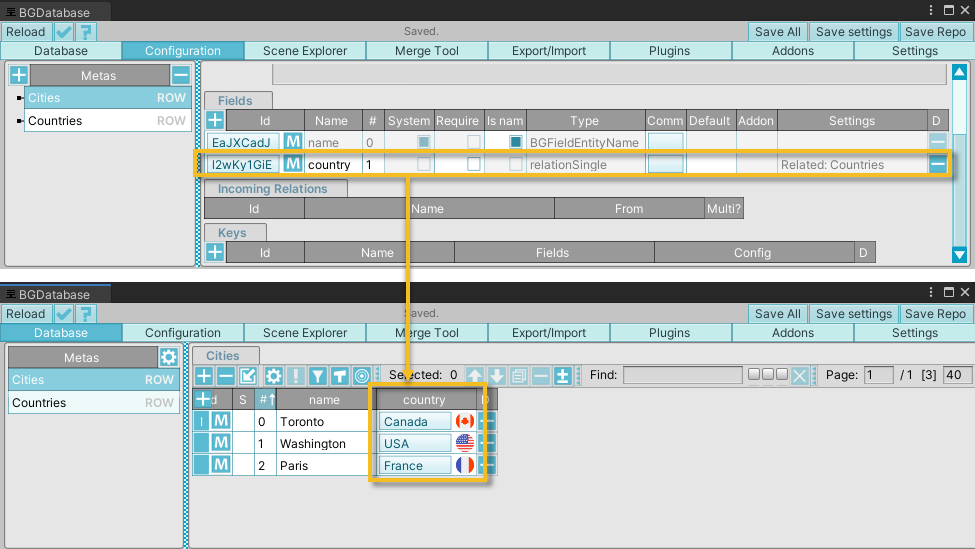
Relational fields are used to reference database rows. These fields store a row's primary keys and use these keys to resolve and return the corresponding database rows when requested. The simplest relational field, relationSingle, functions like a nullable foreign key referencing a single row from a single table.
For example, there are two tables a Cities table and a Countries table. The
Cities table has a
country relationSingle field referencing the Countries table.
Relational fields differ in the number of tables and rows they can reference (read this blog post for more details)
Starting with BGDatabase 1.7.5- viewRelationSingle and viewRelationMultiple fields are recommended over manyTablesRelationSingle and manyTablesRelationMultiple fields (read this blog post for more details)
| Field (relation) | How many tables can be referenced | How many rows can be referenced |
|---|---|---|
| relationSingle | 1 | 1 |
| relationMultiple | 1 | n |
| manyTablesRelationSingle | n | 1 |
| manyTablesRelationMultiple | n | n |
| viewRelationSingle | n | 1 |
| viewRelationMultiple | n | n |
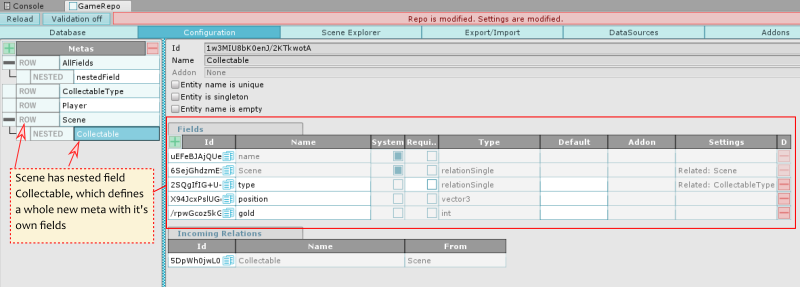
Nested fields (#2)
A nested field is a special field that creates a new meta (table) with a many-to-one relationship to its owner meta.
This allows you to create a linked list where each element represents a row from the nested table.
It is a readonly field (to change its value - delete or add nested entities).
To create a nested entity from C# code, use the special method that accepts the owner of the nested entity BGMetaNested.NewEntity(BGEntity
owner). BGMetaNested is a class for nested tables (to be used instead of generic BGMetaRow)
Technically, a nested table is a standard table with a many-to-one relationship to its parent table, distinguished by two key features:
- To access nested rows, you must first select a parent row using the parent table’s GUI.
- Deleting a parent row automatically deletes all related nested rows, as they are considered an integral part of that parent row.
The comparison between nested and row tables.
Also, you can read more about nested table concept here
Unity scene fields (#3)
Referencing scene GameObjects using objectReference/objectListReference/objectListMultiValueReference fields is
implemented using the same technique as demonstrated in
this example Unity project.
This involves adding a component (available under the "Components" menu as "BansheeGz/Id" and implemented as the C#
class BGWithId) that assigns a unique ID to each object.
BGWithId is a MonoBehaviour component; to access the associated GameObject- use gameObject property.
In the Awake method, the object is added to the internal cache and in the OnDestroy method, it's removed from this cache.
The results depend on which objects are loaded and which are not, and may vary during a play session.
A table describing the fields’ features follows:
| Feature ↓\Field → | objectReference | objectListReference | objectListMultiValueReference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Returns the first loaded GameObject with specified ID | Returns all loaded GameObjects with specified ID | Returns all loaded GameObjects with specified IDs |
| Internal value | Single ID | Single ID | Multiple ID |
| Comments |
These two fields differ in how they use IDs to reference multiple GameObjects.
The objectListReference field uses the single ID value and returns all loaded GameObjects, associated with that ID.
The objectListMultiValueReference field uses multiple ID values and returns all loaded GameObjects associated with those IDs.
|
||
Hashtable (#4)
Hashtable is a dictionary without generic parameters. The following types are supported as keys: int, long, short, byte, string, bool, Guid, enums. The following types are not supported as values: Unity assets, relations, hashtable, nullable structs. Null values are also not supported.
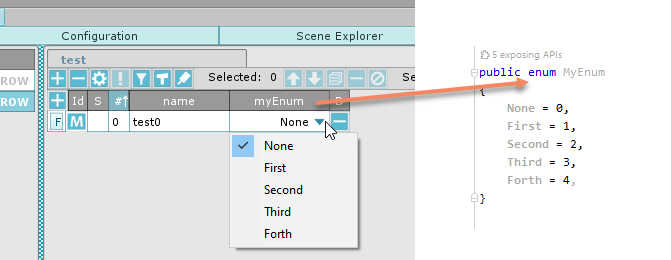
Enum/enumList (#5)
With enum/enumList fields you can reference your own enumerations. Important notes:
-
You need to provide the correct C# enum type name when creating an enum field.
If you are unable to determine the correct C# type name for your enum, use
Type.FullName
property to print enum type name to the console
Debug.Log(typeof(MyEnum).FullName);Enum type name examples
// MyEnum public enum MyEnum { } // MyNameSpace.MyEnum namespace MyNameSpace { public enum MyEnum { } } // MyNameSpace.MyClass+MyEnum namespace MyNameSpace { public class MyClass { public enum MyEnum { } } } - Once enum field is created, changing enum type name, namespace, or underlying type also involves changing enum type stored in the database. If you need to rename the enum type or namespace, refer to this guide. If you need to change underlying enum type (int, short, byte), refer to this guide.
- Values are stored exactly as C# stores them— with numeric values. Consider assigning numeric values to your constants so that you can reorder them without affecting the stored values.
Enums with [Flags] attribute has special GUI, allowing to select multiple constants
Unity Asset Fields (#6)
All these fields are read only.
You can reference any Unity asset (unityObject field can be used to reference any asset).
Available loaders
| Resources | Asset Bundles (obsolete) | Addressables | Addressables by Guid | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recommendations | Use it only if an amount of assets is small. Unity does not recommend to use it (more info) | not recommended under any circumstances | use it if you want database to store asset's address | use it if you want database to store asset's Guid. |
| How asset is loaded | using Resources.Load | using AssetBundle.Load | using Addressables.LoadAssetAsync | |
| Prerequisites | An asset should be placed in one of the "Resources" folders. | an asset should be included into one of asset bundles |
|
|
| Stored value | path, relative to Resources folder | path within asset bundle | asset address | asset Guid |
| Limitations after an asset was referenced from database (otherwise you need to reassign the value) | path/name can not be changed | name can not be changed | an asset address can not be changed, but you can freely move or rename the asset | an asset's Guid can not be changed (it's stored in the corresponding meta file), but you can freely move or rename the asset |
| More information | Read more about Resources folder and asset bundles here | Read Unity's Addressables manual here. To add support for addressables, please, download our plugin and follow setup/use manual at our download page | ||
Third-party YooAsset loader is also available as a plugin
Sprite field and complex assets
Sprite and UnityObject fields support complex assets (when multiple assets are stored in one single file). Sprite fields support spritesheets/atlases. UnityObject field should support other asset types (like FBX file etc.) if you assign correct "Asset Type" parameter while creating UnityObject field. "Asset Type" parameter accepts valid full C# class name (for example UnityEngine.Material)
Optional L2 cache
Asset fields support optional additional cache on top of Unity API. If this cache is enabled Unity API is used to
load the object for the first time; all subsequent reads use the cache to retrieve the object instead of using Unity API.
To enable the cache use the following code: BGAssetsCache.Enabled = true;
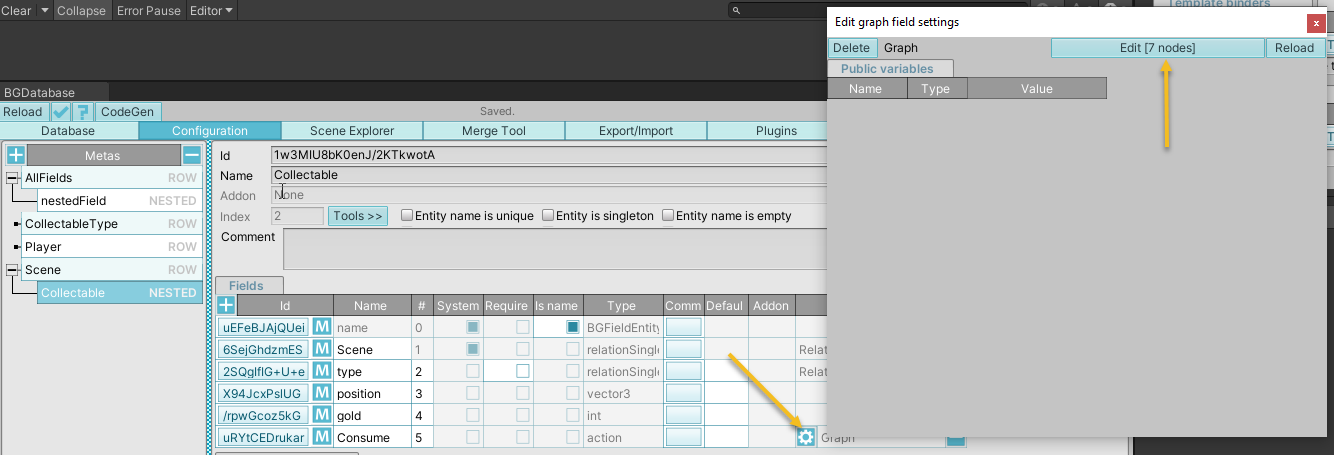
Calculated Fields (#7)
Calculated fields store a graph used to calculate a result value. Graph is edited using graph editor.
Fields can have a default graph (edit via gears icon under "Configuration" tab) and a list of public variables
Each row can 1) override any public variable of default graph and 2) can have its own graph. A more efficient alternative to overriding variables is to use database field values. You can access the current row using the "Special/Get current entity" node.
An Action is a special calculated field that doesn’t return a value but can change database values. To invoke an action, use the Invoke method on the field value.
Programmable Fields (#8)
Programmable fields are alternatives to calculated fields; however, the calculation is implemented with C# code rather than the graph tool. Use these fields only if you want the calculation result to appear in the database GUI; otherwise, you can extend generated classes as described here
To create programmable field, you must provide the name of C# class implementing BGCodedFieldDelegateI<type> interface during field creation. The instance of this class will be used for value calculation
Click to see C# example
using BansheeGz.BGDatabase;
public class CalculateC : BGCodedFieldDelegateI<int>
{
public int Get(BGCodedFieldContext context)
{
var entity = context.Entity;
return entity.Get<int>("a") + entity.Get<int>("b"); // c = a + b
}
}If you want to use events, implement BGCodedFieldDelegateLifeCycleI interface as well
Click to see C# example
public class CalculateC : BGCodedFieldDelegateI<object>, BGCodedFieldDelegateLifeCycleI
{
private BGField myField;
public object Get(BGCodedFieldContext context)
{
var entity = context.Entity;
return entity.Get<int>("a") - entity.Get<int>("b");
}
//this method is called on delegate loading
public void OnLoad(BGCodedFieldDelegateLifeCycleContext context)
{
//add event listeners
myField = context.Field;
var aField = context.Field.Meta.GetField("a");
aField.ValueChanged += FieldValueChanged;
var bField = context.Field.Meta.GetField("b");
bField.ValueChanged += FieldValueChanged;
}
//this method is called on delegate unloading
public void OnUnload(BGCodedFieldDelegateLifeCycleContext context)
{
//remove event listeners
var aField = context.Field.Meta.GetField("a");
aField.ValueChanged -= FieldValueChanged;
var bField = context.Field.Meta.GetField("b");
bField.ValueChanged -= FieldValueChanged;
}
//fire 'c' field value changed
private void FieldValueChanged(object sender, BGEventArgsField e) => myField.FireValueChanged(e.Entity);
}Collection values
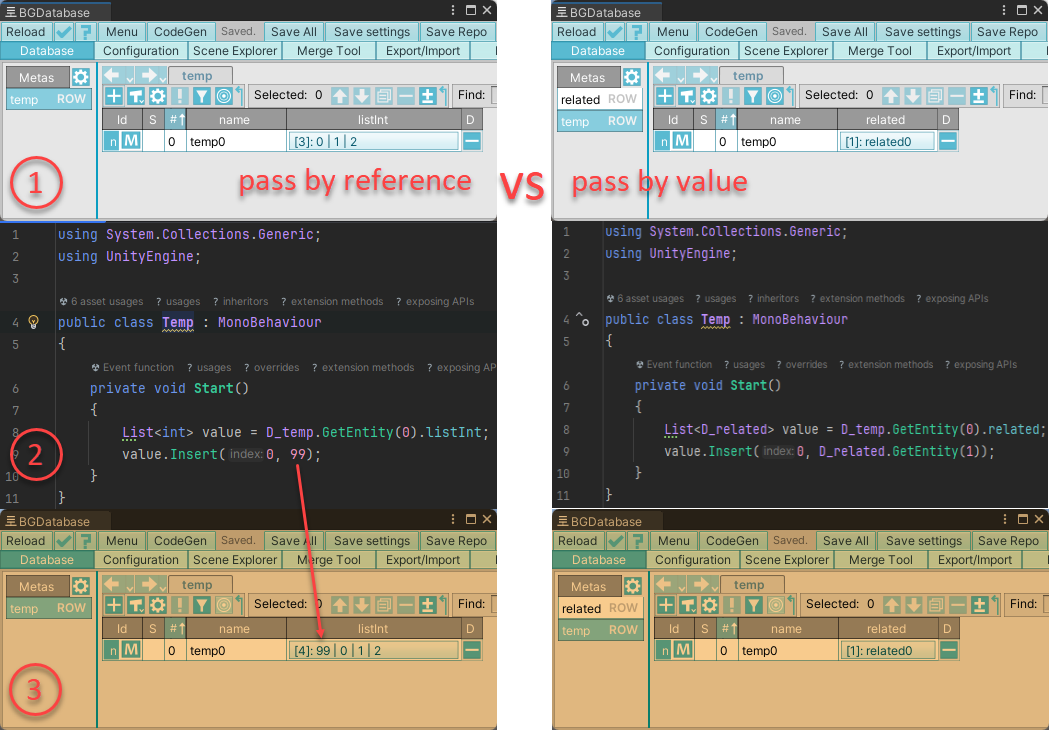
Collection fields may return the result (the list/hashtable) by reference or by value
- Returning by reference means the value stored inside the database is returned. Consequently, changing the collection’s values will actually change the database value without setting a new value.
- Returning by value means a new collection is created when the value is accessed, and it can be modified without changing the database value.
The current strategy is to return a collection by reference whenever possible, and to return the collection by value only when returning it by reference is not feasible (to avoid garbage collection and performance impact)
| Field(s) | Basic API | CodeGen addon |
|---|---|---|
| Lists with primitive values (List<string> etc.) | by reference | by reference |
| Hashtable | by reference | by reference |
| Multiple relational fields (Lists with rows values) | by value | by value |
| Enum list | by value | by reference |
Example using CodeGen add-on with "classes prefix"= "D_"